Introduction
Pets bring immense joy, but like us, they’re prone to health concerns that can affect their happiness and well-being. At Barkbliss, we know being proactive about pet health is key—not waiting until your pup or cat shows visible signs of illness. This comprehensive guide walks you through the most common health issues seen in dogs and cats, and provides clear, preventative strategies to keep your pet thriving year-round. We’ll explore:
- Digestive disturbances (vomiting, diarrhea)
- Skin and coat problems (allergies, dryness, infections)
- Dental disease
- Joint and mobility disorders
- Ear infections and eye concerns
- Parasites (fleas, ticks, worms)
- Behavioral and stress-related health issues
Each section includes:
- Signs to watch for
- Underlying causes
- Evidence-based prevention
- Practical tips tailored for homes, breeds, age groups
- Lifestyle and environmental factors
Aligned with veterinary standards and expert guidance, this post empowers you to act before issues escalate—helping your pet enjoy a happier, healthier life. Let’s dive in.
1. Digestive Disturbances
A. Overview & Signs
Vomiting and diarrhea account for 10–20% of vet visits. Key signs include:
- Acute vomiting/diarrhea: One-off incidents
- Chronic GI upset: Recurring or persistent symptoms
- Accompanying signs: decreased appetite, lethargy, weight loss, blood/mucus

B. Common Causes
- Dietary indiscretions (garbage, table scraps)
- Sudden food changes
- Food allergies or intolerances
- Infections (bacterial, viral, parasitic)
- IBS, pancreatitis, inflammatory bowel disease
- Toxin ingestion (e.g., xylitol, lilies for cats)
C. Prevention Strategies
- Consistent, quality diet – Stick to vet-approved or therapeutic food.
- Proper portion control – Follow feeding guidelines, consider blends to avoid overeating.
- Safe food handling – Avoid unsafe human foods; vet-check before feeding anything new.
- Gradual transitions – Mix new food over 7–10 days.
- Avoid scavenging – Use secure trash cans and leashes.
- Hydration vigilance – Ensure easy access to clean water.
- Parasite prevention – Year-round deworming and fecal monitoring.
- Supplement support – Probiotics with vet guidance.
- Prompt attention – Early vet visits for chronic issues to prevent progression.
2. Skin & Coat Problems
A. Signs & Impact
These account for up to 25% of vet visits. Look for:
- Excessive scratching, biting, licking
- Redness, inflammation, scabs, bald patches
- Dandruff or oily buildup
- Lumps, bumps, inflamed pores

B. Common Causes
- Seasonal/environmental allergies (pollen, dust, mold)
- Food sensitivities
- Flea allergy dermatitis
- Ideal bacteria overgrowth (hot spots, yeast)
- Dry air or improper grooming
C. Prevention Tactics
- Allergy management – Regular baths with hypoallergenic shampoo; consider allergy testing for chronic cases.
- Flea/tick control – Use vet-recommended treatments year-round.
- Tailored diet – Grain-free or limited-ingredient diets under vet guidance.
- Proper grooming – Routine brushing and bathing; don’t overwash.
- Humidifiers – Use in dry climates/rooms.
- Topical care – Soothing ointments or medicated sprays.
- Vet follow-up – Early treatment of infections or skin conditions.
3. Dental Disease
A. Scope & Symptoms
By age 3, ~80% of dogs and 70% of cats have some dental disease:
- Bad breath, gum redness, bleeding
- Tartar buildup, loose teeth, difficulty eating
- Behavioral changes (pawing face, irritability)

B. Causes
- Poor home dental care
- Soft/humid diet patterns
- Breed-specific structure issues
- Genetic predispositions
C. Prevention Protocol
- Daily brushing – Use pet-specific toothpaste and soft brush.
- Dental chews – Approved by Veterinary Oral Health Council (VOHC).
- Water additives – Enzymatic or chlorhexidine-based.
- Regular vet cleanings – At least annually or as recommended.
- Monitoring – Check teeth, gums, breath weekly.
- Dietary support – Prescription dental diets for scaling + additives for oral hygiene.
4. Joint & Mobility Disorders
A. Symptoms & Affected Demographics
Common in large breeds and senior pets—look for:
- Stiffness, slower walking
- Difficulty rising/jumping
- Decreased activity or play
- Lameness, swollen joints

B. Root Causes
- Aging-related arthritis
- Hip/elbow dysplasia
- Injuries or excessive strain
- Excess bodyweight
C. Prevention & Management
- Maintain healthy weight – Regular BCS monitoring and controlled portions.
- Low-impact exercise – Swimming or gentle walks.
- Joint supplements – Glucosamine, chondroitin, omega-3 (vet-approved).
- Physical therapy – Hydrotherapy and gentle massage.
- Comfort aids – Orthopedic bedding, ramps.
- Monitor activity – Manage high-impact play for at-risk breeds.
- Advanced care – Pain management with NSAIDs or alternative therapies when needed.
5. Ear & Eye Conditions
A. Common Signs
Ear issues: shaking head, scratching ear base, odor, redness, discharge
Eye concerns: tearing, squinting, cloudiness, discharge, redness
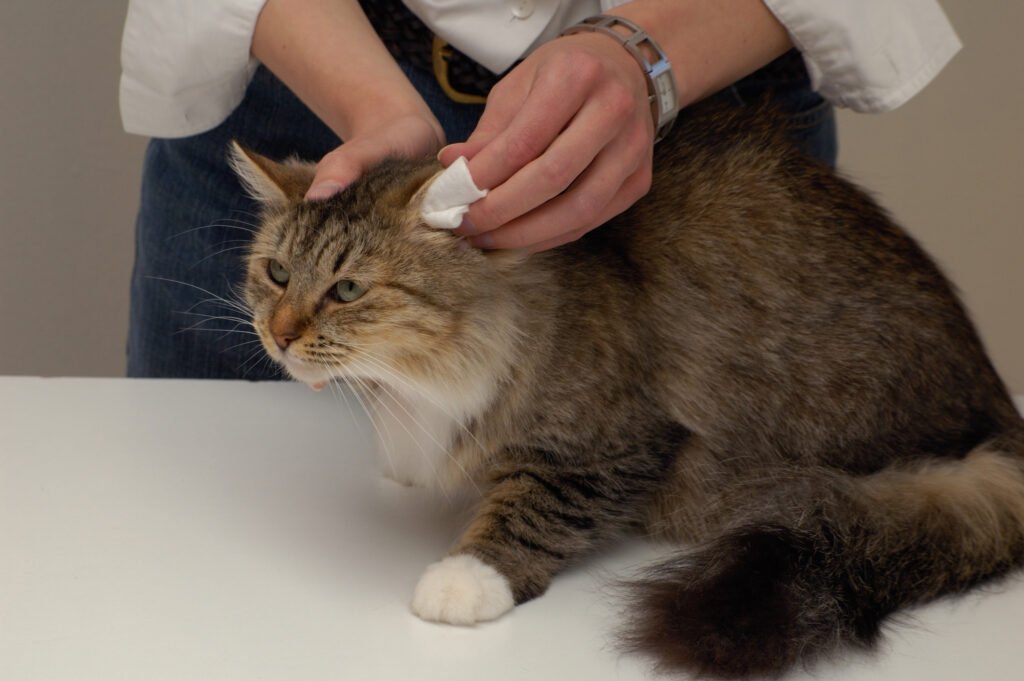
B. Causes
- Allergies
- Moisture retention
- Ear structure (droopy ears)
- Tear duct issues, infections, injury
- Genetics (like cherry eye, glaucoma)
C. Prevention Measures
- Regular inspection – Check weekly, especially after baths/swims.
- Safe cleaning – Use vet-recommended wipes; never insert deep into canal.
- Keep dry – Gently pat dry inside ears post-swim.
- Professional intervention – Vet cleaning or corrective surgery if recurrent.
- Prescription meds – For diagnosed infections or sensitivities.
- Eye hygiene – Clean discharge with saline and cotton pad; consult vet for abnormalities.
6. Parasites
A. Fleas, Ticks, Worms & Prevention
Parasite-related issues include skin irritation, serious disease transmission, and gut issues.

Fleas & Ticks
- Use year-round topical/oral preventives
- Check after outdoor time; remove ticks promptly
- Treat indoor environment regularly
Internal Parasites
- Deworm puppies/kittens regularly; consult vet for roundworms/hookworms
- Perform fecal checks every 6–12 months
Vector-Borne Infections
- Protect from heartworm, Lyme, Ehrlichia depending on location
- Consider annual blood testing
7. Behavioral & Stress-Related Health Issues
A. Link Between Behavior & Health
Chronic stress can impact gut, skin, heart, and overall wellness:
- Causes include confinement, lack of enrichment, separation anxiety
- Symptoms: compulsive behaviors, excessive grooming, appetite shifts

B. Prevention Strategies
- Environmental enrichment – Rotational toys, cat trees, chew toys
- Regular exercise – Walks, play, training sessions
- Safe spaces – Quiet areas or crates used positively
- Routine adherence – Feeding and potty schedules
- Training/socialization – Manage anxiety through exposure
- Professional support – Consult behaviorists for chronic stress
Conclusion
Awareness of common pet health issues empowers you to prevent problems before they worsen. From digestive care and skin/coat management to dental health, joint support, and parasite defense, proactive measures shape a longer, happier life for your pet. At Barkbliss, we advocate for a balanced routine of veterinary care, daily vigilance, mental well-being, and enrichment. Every pet deserves a thriving life—stay attentive, stay informed, and let your bond deepen.
For personalized advice, always consult your vet. If you’ve implemented these strategies, share your success story on Barkbliss—we love celebrating healthy pets and happy homes.

